Sharing tips in developing team work plans
- by Alex Antonatos
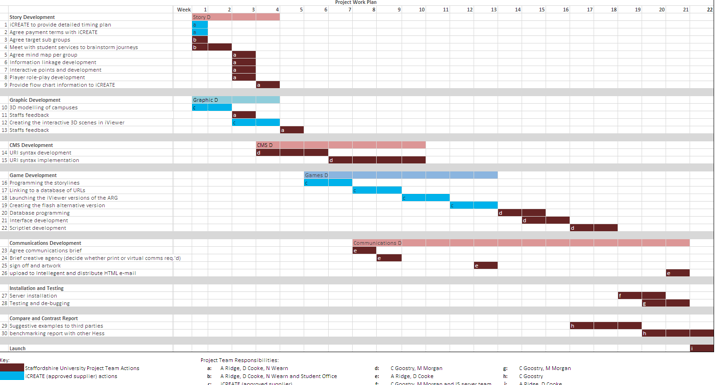
The project manager determines whether any project management activities should be included in the team workplan. Be specific when defining the skills, background, and experience required for each task. This allows you to make more accurate work assignments (role) to team members and minimizes problems caused by assigning a team member to inappropriate responsibilities.
- Do not create artificial contract deadlines that are actually target dates. Dates that are deadlines should be specified in the contract. Dates that are not in the contract are typically target dates, which are objectives or goals that may move.
- Workplan development follows either a Critical Chain or a Critical Path method.
Critical Path Versus Critical Chain Approach
- Critical Chain Approach—Focuses on the final deliverable due date for the project rather than on interim due dates. Activity durations are estimated with no safety factor or time buffer included. Instead, Project Management incorporates safety into the Workplan to protect the final due date.
- Critical Path Approach—Project duration is driven by the interim activities that must be completed, the availability of resources, and safety factors built in to each task or activity.
- The Critical Chain approach is concerned with the latest date that a task or activity may be started to meet the final due date of the project.
- In the Critical Path approach, a project start date must be determined. If a start activity is not obvious, create an activity entitled "project start" or "initiate project" to indicate that the project does have a real start time.
- In a Critical Path approach, resource availability affects the duration of tasks, milestones, and the overall project completion date. The more resources available, the shorter the durations. In the Critical Chain approach, the required completion date determines the resources required. If resource availability is limited, the scope of work must be re-evaluated and possibly reduced to meet the completion date. In either case, the resource model is updated to reflect actual resource assignments.
- In the Critical Path approach, identify activities that can begin immediately (that is, they have no predecessors), and make the start activity their predecessor.
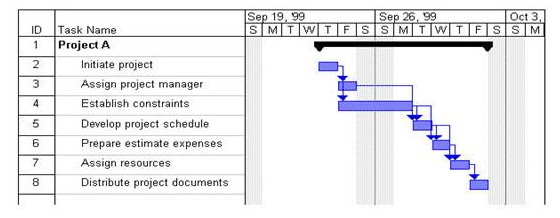
- Using the activity list and dependency information, sequence the remaining activities. A simple activity-sequencing example is shown below.
- Identify the finish activity for the project. For example, include a milestone called "project end." Every activity in the project needs to be completed before this milestone is reached.
- Review any guidelines, practices, or procedures for preparing a Workplan. Verify that the WBS is in line with the Project Charter, and update sections of the Project Charter as necessary.
- The baseline Workplan and framework documents for the standard methodology can be used as a starting point. Also refer to any lessons learned documents and other, similar workplans. Expert advice or opinion is also valuable when performing this step.
- Workplan development is an iterative process because the resulting schedule needs to be compared with the scope and other constraints to verify its feasibility.
- The Workplan should be reviewed frequently. The best project managers continually try to assess what can go wrong and perform up-front analysis on the schedule. Clearly, project constraints and objectives can change; therefore, schedule analysis should be an ongoing activity.
- Obtain Workplan buy-in from all key team members. In many ways, this is more important than formal approval, because team members who are committed to the Workplan are more likely to put forth the effort required to adhere to it than those who are not.
- Review of deliverables includes reviewing action items and verifying actions to improve performance, revisiting and refining the Workplan, and acknowledging that the plan meets the expectations of the management team.
- Reviewers should typically include the project sponsor and the organization. They may also include other organization authorities who have direct influence or need-to-know responsibilities. Reviewers can vary from project to project but should be determined early in the project life cycle.
- To avoid delays in the overall project schedule, the time allotted for reviewing the Workplan should be formally communicated to the project sponsors before submission for approval.
Activity Sequencing 1
|
Activity ID |
Activity |
Immediately Preceding Activity |
|
1 |
Project A |
|
|
2 |
Initiate project |
- |
|
3 |
Assign project manager |
2 |
|
4 |
Establish constraints |
2 |
|
5 |
Develop project schedule |
3, 4 |
|
6 |
Prepare estimate expenses |
4, 5 |
|
7 |
Assign resources |
5, 6 |
|
8 |
Distribute project documents |
7 |
Activity Sequencing 2
Workplan Standards and Guidelines
Workplan Review
Please share your thoughts and tips on workplans